- Date added:
- Jan 02, 2025 | Last update check: 1 minute ago
- Integrations:
- Autodesk Construction Cloud (ACC), BIMcollab, Enscape: Simple real-time visualization plugin, FormIt, Navisworks, Rhino
- Licence:
- Trial | Buy Now
- Runs on:
- Windows 10 64-bit / 11 See Autodesk’s Product Support Lifecycle for support information
Revit is a robust architectural, structural and MEP design and documentation package that has become the standard BIM software for architects and building design professionals. It is the tool designed for architects and constructors who want to immediately implement all the parameters into a 3D model. The basis of the Autodesk Revit application is the Building Information Modeling, a comprehensive design process that starts by designing the concept of the building, and ends up by creating the project documentation for construction. It enables efficient collaboration of project teams, indicates errors and ways to eliminate them and carries out all simulations and analysis in real environment.
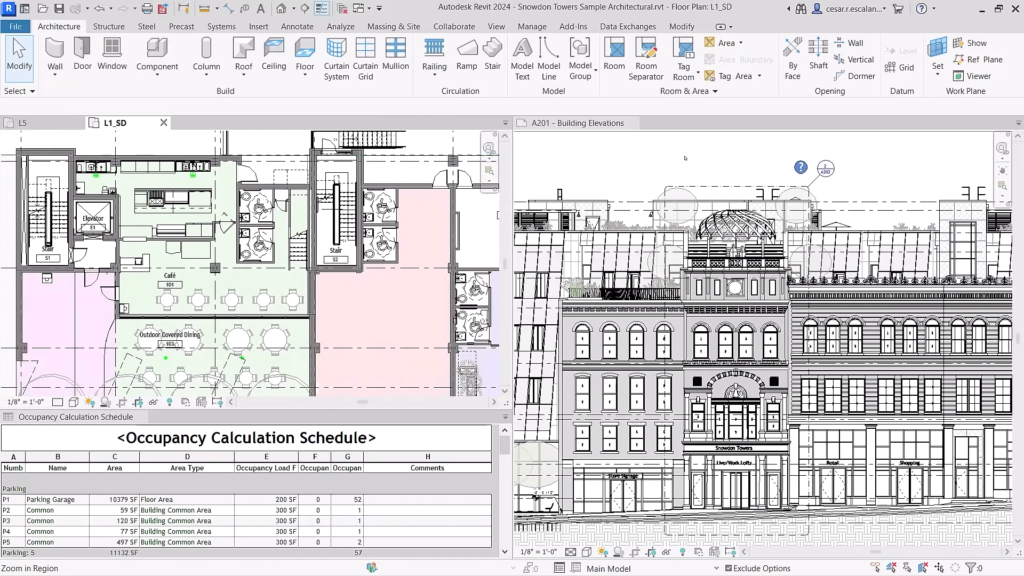
Using Revit you can easily create walls, columns, floor slabs, doors, windows, and other building elements. But using Revit is not just about modeling. You can annotate your drawings with text, dimensions, and other standard architectural symbols, generate live schedules of just about any part of your building, create legends, construction details, and compose sheets for printing out your document sets.
Until version 2017, Revit was the product family that consisted of three software: Revit Architecture, Revit MEP and Revit Structure. From version 2017, Revit merged into one box and replaced these stand-alone products.
Integration
In the BIM workflow, Revit serves as a central hub for creating BIM models. Revit is well integrated into both the upstream and downstream parts of the BIM workflow.
Upstream integration. In the upstream process, Revit works with various 3D modeling, analysis and visualization tools like Rhino, FormIt, Forma, and Enscape. These tools are used in the early stages of design, allowing architects to create and explore multiple concepts. Revit’s integration with these tools facilitates a smooth transition from conceptual design to more detailed design development within the Revit environment.
Downstream integration. In the downstream process, Revit integrates with tools like Navisworks, Autodesk Construction Cloud (ACC), and BIMcollab. These tools are used for clash detection, coordination, issue management, takeoff and estimation, and simulation, which are crucial in the construction phase. Revit’s integration with these tools allows for effective BIM and project management as well as visualization of important construction factors.
Revit’s integration with cloud services like ACC ensures collaboration and data sharing among project stakeholders during the entire project lifecycle. While Revit is used in conceptual and developed design stages, it achieves its full potential in the construction phase of the project. Its high interoperability helps AEC professionals bridge the gap between the design and construction phases.
It’s worth noting that there are many add-ins for Revit developed by third parties.
Pricing plans
Autodesk Revit offers a 30-day free trial and several pricing plans including monthly, annual, and three-year subscriptions. For occasional users, the Autodesk Flex token-based system provides pay-as-you-go access. Additionally, the AEC Collection includes Revit along with other essential Autodesk tools for professionals in architecture, engineering, and construction. The AEC Collection is cheaper than subscribing to Revit and AutoCAD separately, making it a cost-effective option for professionals who need both Revit and AutoCAD, along with other software tools provided in the collection.
Typical workflow
- BIM management: Working in Revit is inseparable from the BIM process. It means establishing BIM standards, protocols, roles, and collaboration frameworks. This step involves setting up the project in Revit, project templates and families.
- Conceptual design and analysis: Tools like Rhino, FormIt, and Forma are used to create initial design concepts and perform early-stage analysis. These conceptual models are then imported into Revit for further development.
- Design development: In Revit, detailed architectural, structural, and MEP components are added, refining the conceptual designs into detailed BIM models.
- Central hub for BIM models: Revit serves as the central hub for creating, managing, and sharing BIM models. ACC supports real-time collaboration and data updates.
- Coordination and clash detection: Models are integrated with tools like Navisworks for clash detection and coordination, identifying and resolving conflicts between different building systems.
- Issue management: Tools like BIMcollab are used to document, track, and resolve issues identified during model coordination, directly within the Revit model environment.
- Construction documentation: Detailed construction documents, including plans, sections, elevations, and schedules, are generated from the Revit model, guiding on-site construction activities.
- Project handover: The final BIM model and associated documentation are handed over to the client and facility managers, providing a valuable resource for future maintenance, renovations, and facility management.
What’s new
Revit 2025.4
- Integrated Dynamo 3.4. This update includes Dynamo 3.4, featuring an improved Package Manager that defaults to compatible package versions based on author-assigned compatibility information.
- Improved Add-ins manager. Administrators now have the ability to control which add-ins users can enable or disable, providing better management of the Revit environment.
- Improved PDF export. The performance of background PDF export has been improved, with up to a 50% reduction in initialization time.
Revit 2025.3
- Improved Add-ins manager. Easily activate or deactivate plugins without uninstalling, and view load times for each plugin.
- Compound elements: Duplicate layers in compound elements, including walls, floors, roofs, etc., for efficient type creation and modification.
- Other improvements: Re-centering for room reference line, in-canvas spell check for text notes, and a real-time status view for background PDF exports.
Revit 2025.2
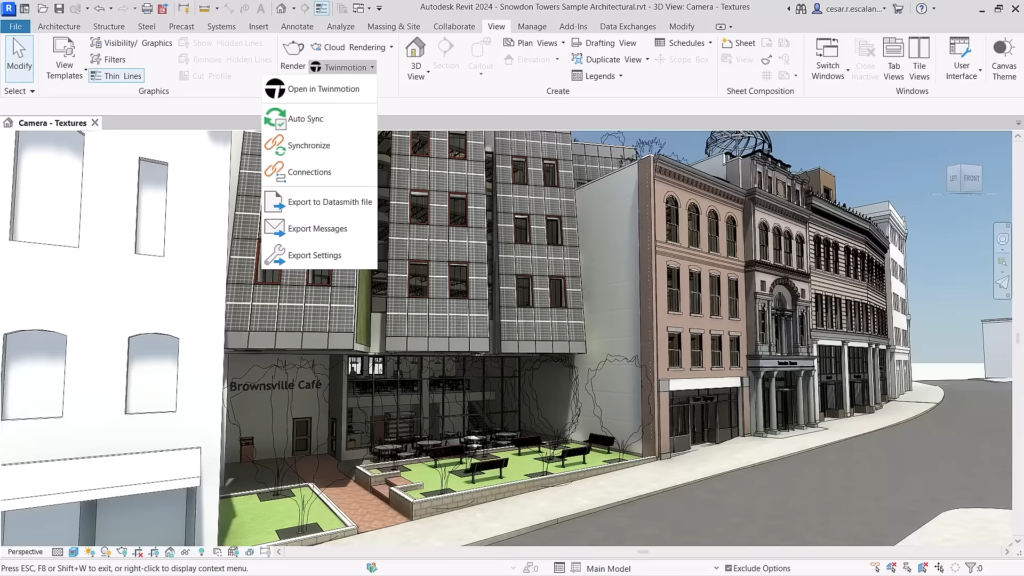
- Twinmotion Substitution: Added a Twinmotion Substitution parameter to define Twinmotion assets for Revit family types, allowing automatic substitution of family geometry when opening in Twinmotion or exporting to Datasmith.
- Project Browser tabs: Introduced tabs to display different view types separately, enhancing navigation and reducing scrolling.
- Manage Links UI: Modernized the user interface of the Manage Links dialog.
- Structural enhancements: Added a Weight parameter for structural steel columns and beams, improved volume calculation, and the Length parameter for structural columns can be used in schedules and tags.
- Export PDF: Resolved an issue where items from linked files were missed during background PDF export.
Revit 2025.1
- Enhanced Wall Joins control: In the canvas, you now have the ability to directly control how walls join together. By selecting a wall, you can adjust the join at the end of the wall.
- Enhanced Toposolid Modify mode: A new feature improves contour readability during editing by getting rid of folding lines.
Revit 2025
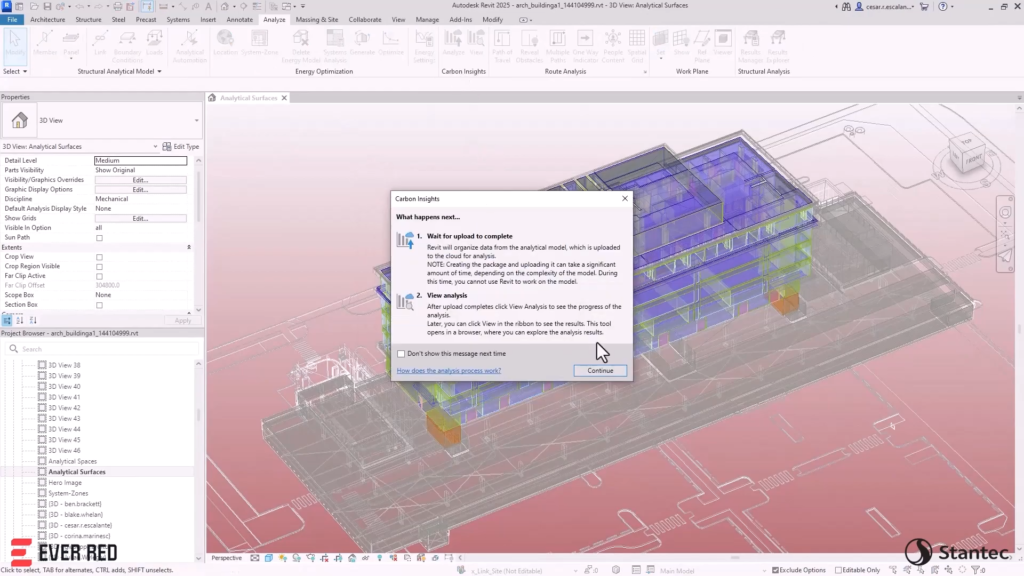
Revit 2025 features Total Carbon Analysis, focusing on sustainability and environmental impact, as well as improved modeling capabilities like Toposolid by Face, arrays with zero or single element, and profiles with multiple closed loops.
Core & Architecture
- Total Carbon Analysis: Estimation of both embodied and operational carbon impacts from the beginning of the design process (using Autodesk Forma and Carbon Insights).
- Project Management enhancements: Introduction of Sheet Collections for efficient sheet organization, flexible sheet groups, and improved search within the Project Browser.
- Enhanced data exchange: Simplified IFC export with IFC Category Mapping, support for STEP file linking and exporting, and updated gbXML schema.
- Site design enhancements: New “Toposolid by Face” tool to create Toposolids from mass slope surfaces, improved excavation and grading alignment, new “Toposolid Smooth Shading” tool, and new Dynamo nodes for automating Toposolid creation.
- Modeling capabilities: More efficient and flexible modeling with automatic wall joining and perforation of joined walls by doors and windows, and detailed modeling of curtain wall mullions (profiles with multiple closed loops). Improved arrays in families (create single element arrays and empty arrays).
- Collaboration and coordination: New “Coordination Model Changes” palette for precise tracking of modifications and improved coordination with Autodesk Docs.
Structure
- Concrete design: New features for rebar modeling and documentation, like parametric rebar slicing, preventing unintended modifications to bars, and creating more complete shop drawings.
- Steel design: Enhancements to the analytical model, detailed steel design features, simplified automation of steel connections, and the capability to split steel framing in columns with connections.
MEP
- MEP analysis: Enhanced support for operating schedules and analytical data, and new analytical model categories (analytical duct and pipe segments).
- Fabrication data management: Improved editing part geometry and data (add and remove type name), improved search functionality, and the ability to upload and assign images to parts.
Gallery
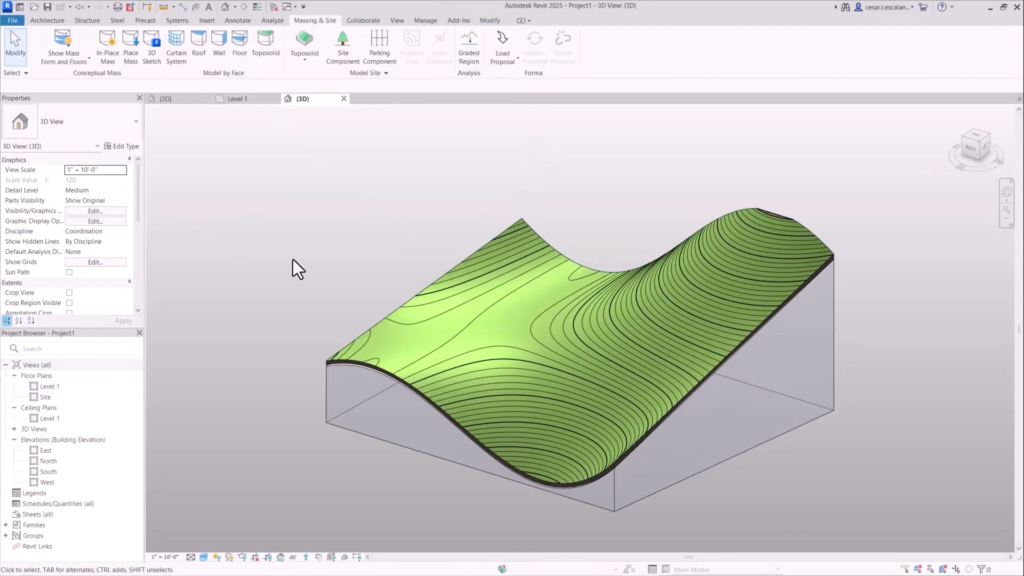
Revit 2025: Model complex topographies with Toposolid by Face.
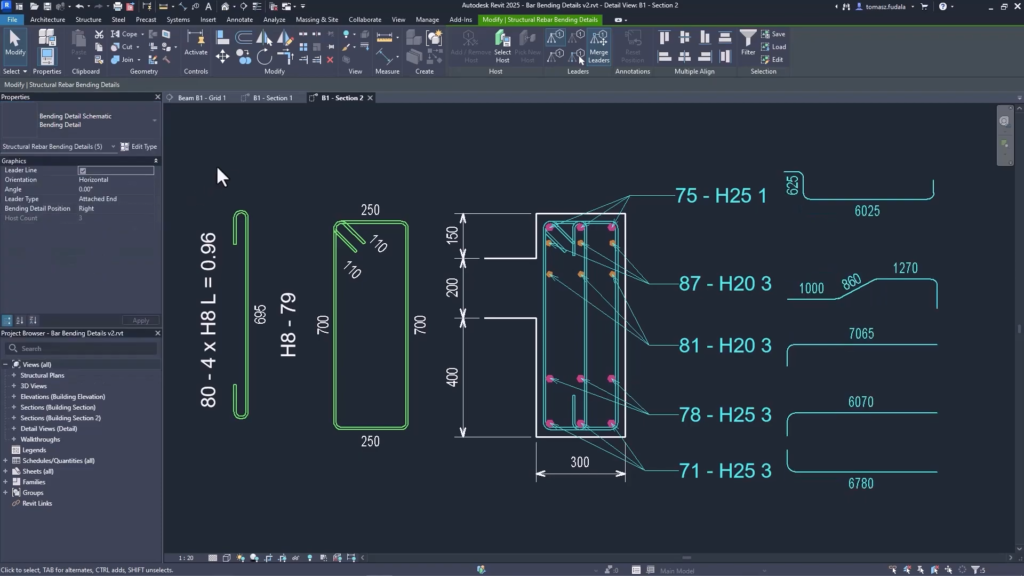
Revit 2025: Improved rebars to create detailed fabrication drawings.
Revit 2024
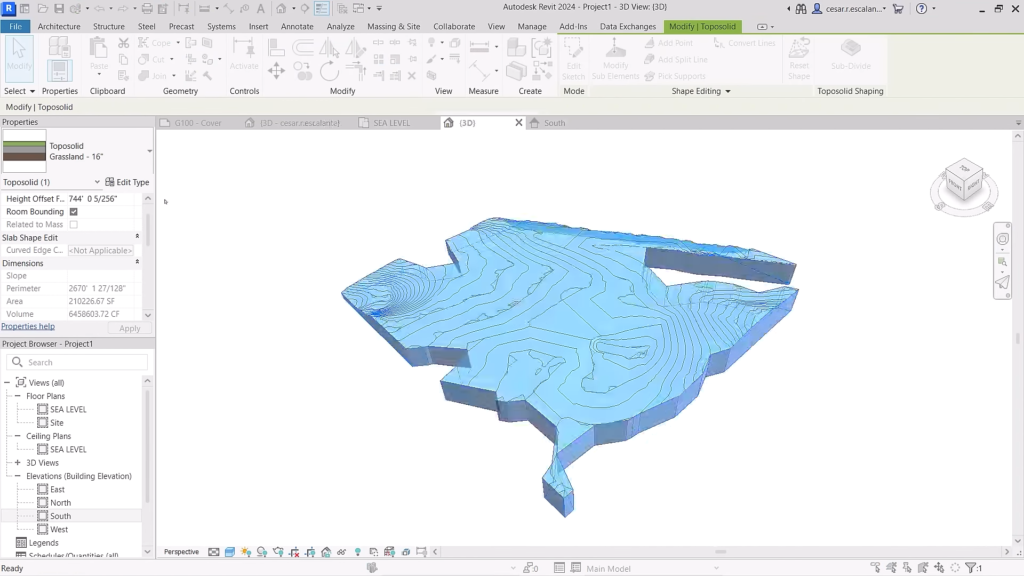
Revit 2024: Site modeling capabilities are improved with toposolids. ©Autodesk
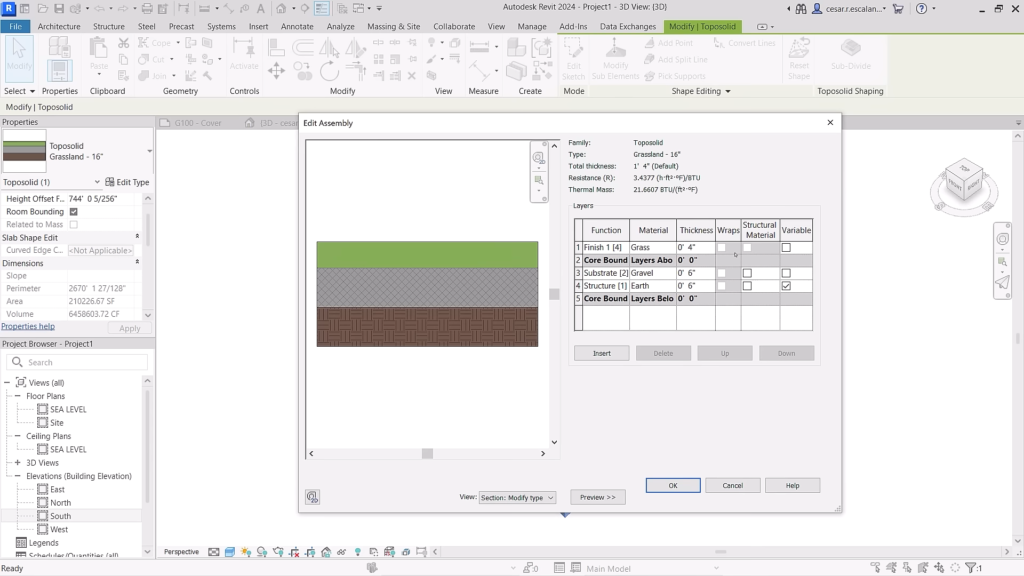
Revit 2024: Toposlids have compound layers and type/instance parameters. ©Autodesk
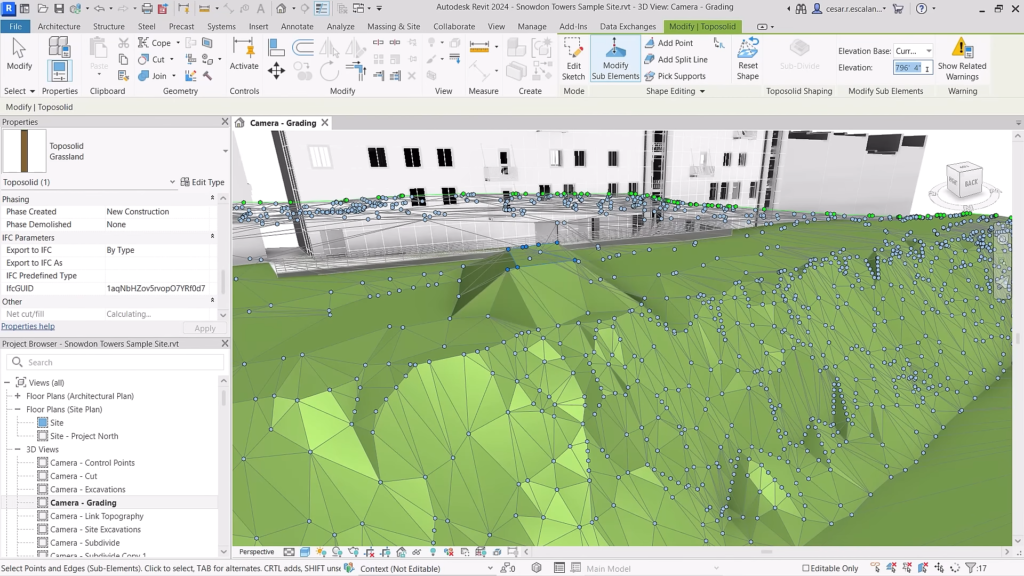
Revit 2024: Toposolids are similar to shape-edited floors. ©Autodesk
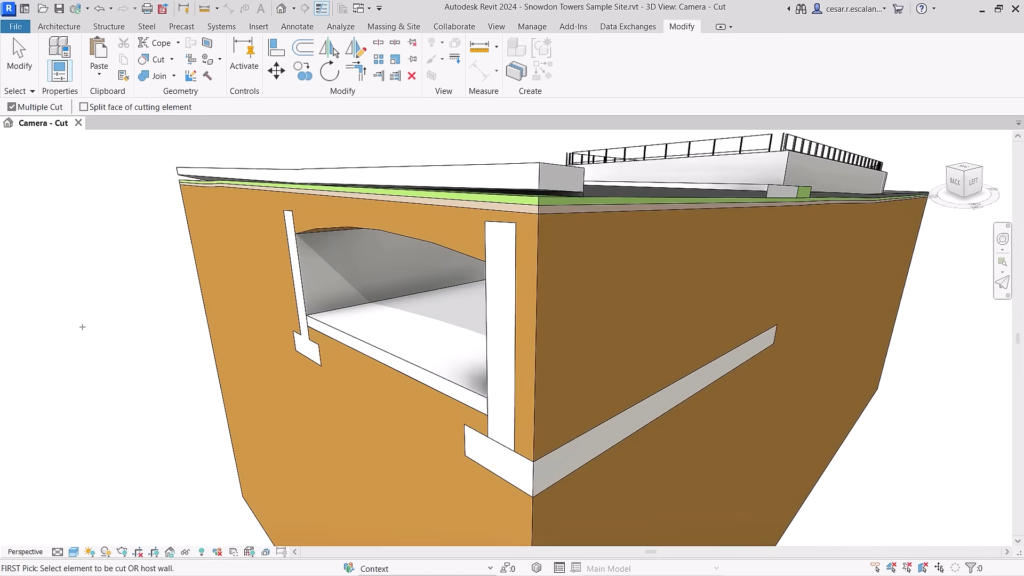
Revit 2024: Finally you can easily create horizontal holes and tunnels, as well as join topography with building elements. ©Autodesk
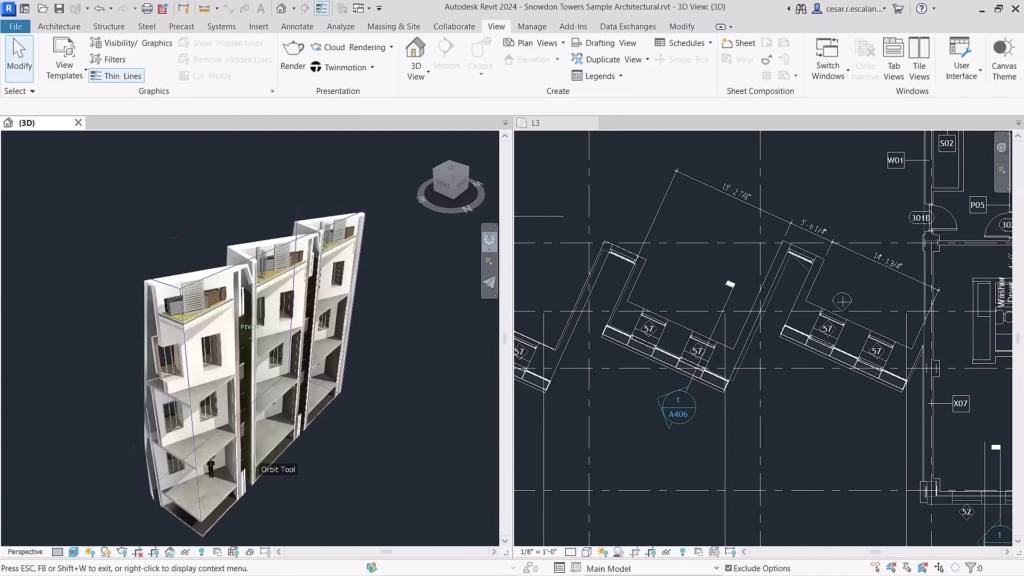
Revit 2024: AutoCAD-style dark interface. You can set it separately for the user interface and the main window. ©Autodesk
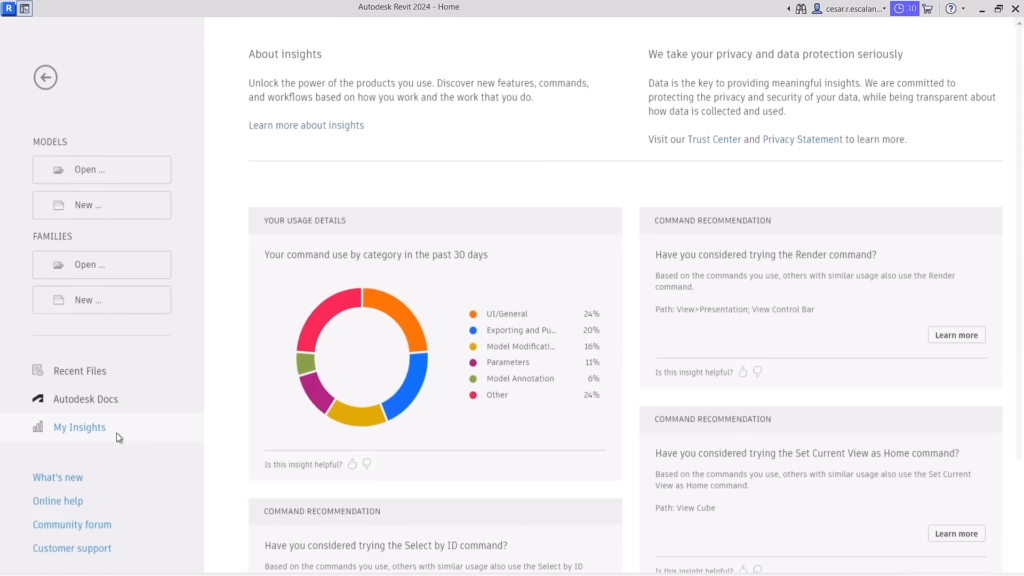
Revit 2024: My Insights panel displays command usage details and recommendations. ©Autodesk
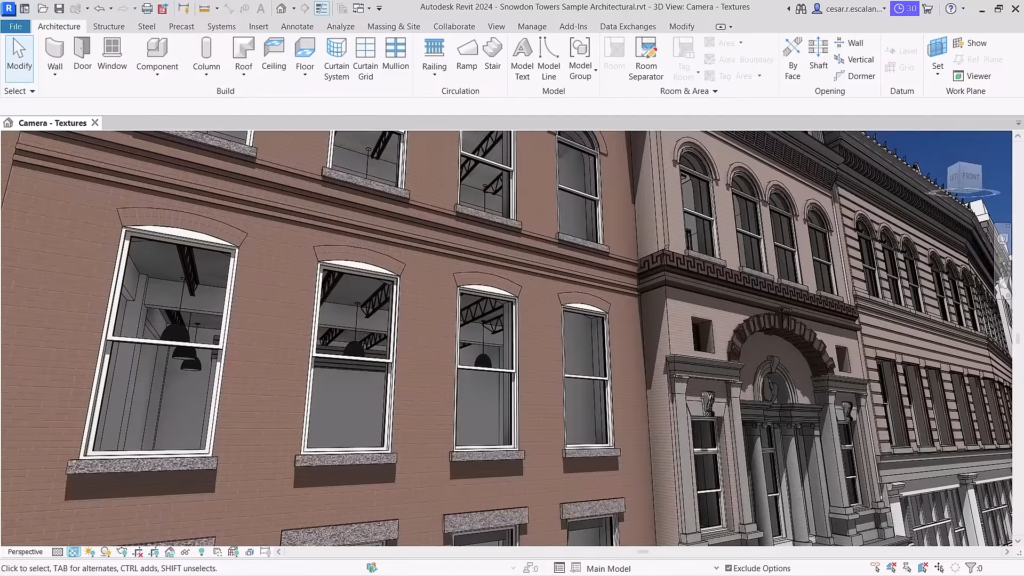
Revit 2024: New “Textures” visual style (between “Consistent Colors” and “Realistic”). ©Autodesk